Dietary fat is a macro nutrient that plays a crucial role in our health. Due to structural differences different fats have different characteristics. There are two types of fat according to the health impact. Those are healthy fat (good fat) and Unhealthy fat (Bad fat)
Good Fat
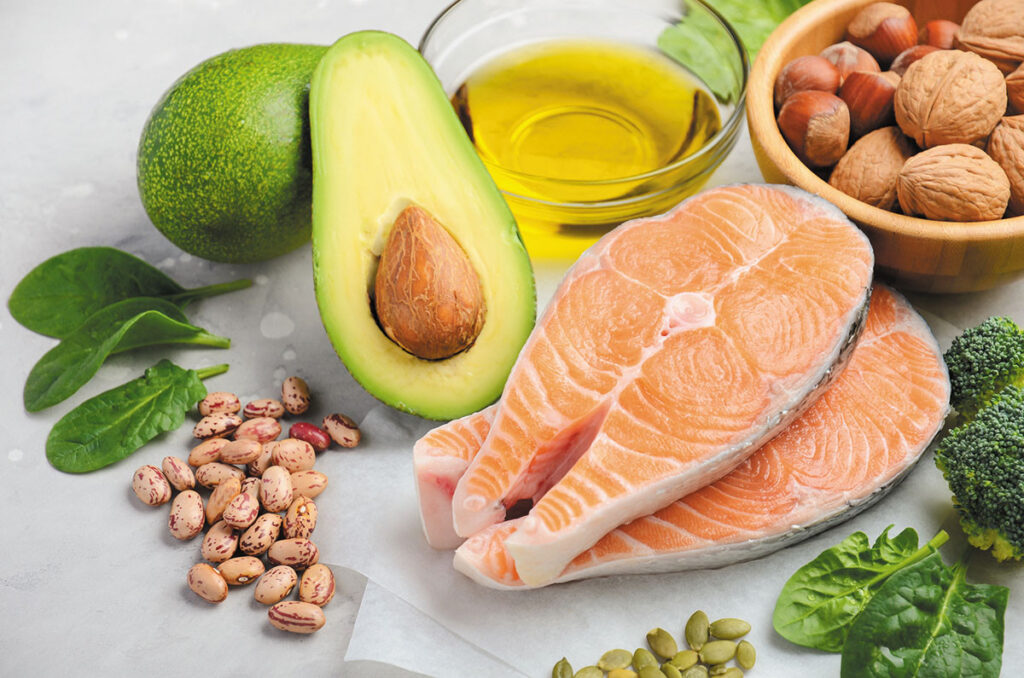
- Monounsaturated Fats: These fats are known for their heart-healthy benefits. They can help reduce bad cholesterol levels (LDL cholesterol) and lower the risk of heart disease. Food sources of monounsaturated fats include olive oil, avocados, nuts (such as almonds, peanuts, and cashews), and seeds (like sunflower seeds and pumpkin seeds).
- Polyunsaturated Fats: These fats also have heart-protective properties and include two important types; omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish (like salmon, mackerel, and trout), flaxseeds, and walnuts, are particularly beneficial for reducing inflammation and supporting brain health. Omega-6 fatty acids are found in vegetable oils like soybean oil and corn oil.
- Unsaturated Plant Oils: Vegetable oils such as olive oil, canola oil, and peanut oil are generally considered healthy when used in moderation. They are a source of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats and can be used for cooking or as salad dressings.
- Saturated Fats (in moderation): Not all saturated fats are necessarily harmful. Some sources of saturated fats, like those from coconut oil, may have health benefits when consumed in moderation.

Bad fat
Bad fats, also known as unhealthy fats, are types of dietary fats that can have adverse effects on health when consumed in excess. They are associated with an increased risk of heart disease, obesity, and other health problems.
- Trans Fats: Trans fats are artificial fats created through a process called hydrogenation, which turns liquid oils into solid fats. Trans fats are found in many processed and fried foods, such as fried fast food, commercial baked goods (cakes, cookies, pastries), and some margarine and vegetable shortening. Trans fats are particularly harmful as they raise levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol while lowering HDL (good) cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Saturated Fats (in excess): Excessive intake of saturated fats from sources like red meat, full-fat dairy products (butter, cheese, whole milk), and processed meats (sausages, bacon) can increase LDL cholesterol levels and contribute to heart disease. It’s important to limit the consumption of saturated fats.
Consuming too many total calories from fats, even from healthier sources like monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fats, can lead to weight gain and obesity if not balanced with other nutrients and overall calorie intake.